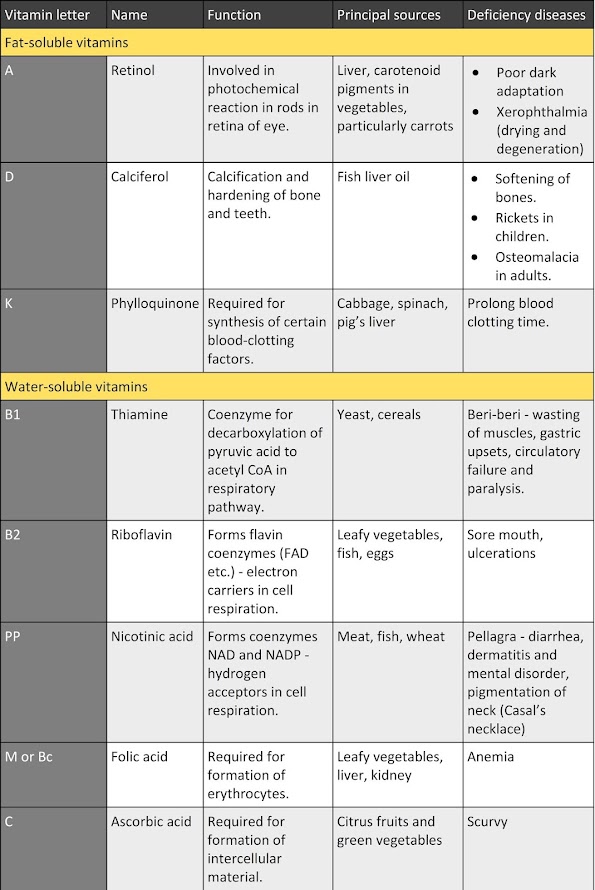
1. Macromolecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
2. The building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids are called nucleotides.
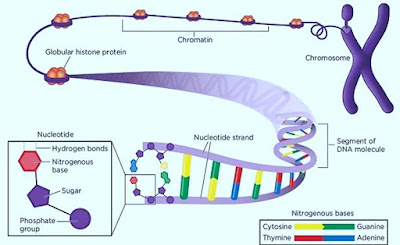
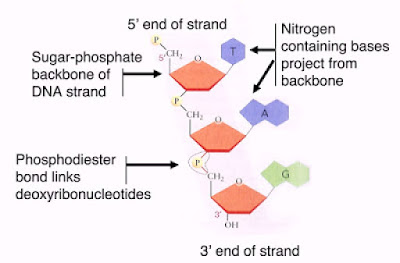
3. Each nucleotide consists of three parts:
- A 5-carbon sugar or pentose
- A phosphate group
- A nitrogenous base
 |
| Structure of nucleotide |
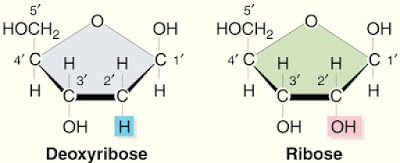
4. 2 types of pentose sugars
- ribose
- deoxyribose
5. Nitrogenous base
- adenine (A)
- guanine (G)
- cytosine (C)
- thymine (T)
- uracil (U)
6. Importance: store & transmit hereditary (genetic) information.
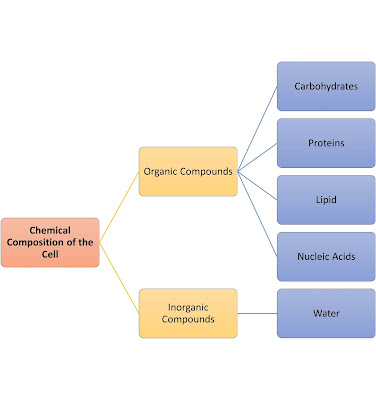
7. There are 2 types of nucleic acids:
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
1. DNA contains deoxyribose sugar.
2. Nitrogenous base groups for DNA - A, T, G, C
3. Consists of 2 polynucleotide strands twisted around each other in the form of a double helix.
4. DNA is found in the nucleus, mitochondrion & chloroplast.
5. Importance: carries the genetic code; to store genetic information
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
1. RNA contains ribose sugar.
2. Nitrogenous bas groups for RNA - A, U, G, C
3. Consists of single-stranded polynucleotide chain, shorter than DNA.
4. RNA is found in nucleus & cytoplasm.
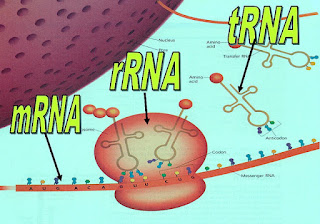
5. 3 types of RNA:
- messenger RNA (mRNA)
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- transfer RNA (tRNA)
6. Importance: involve in protein synthesis
 |
| RNA and DNA structures |