Carbohydrate - Disaccharides
1. General formula: C12H22O11
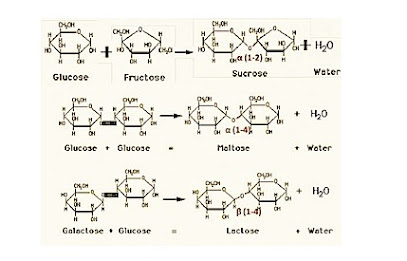
2. Formed during condensation of 2 hexose molecules:
- α-glucose + α-glucose → maltose + water
- α-glucose + galactose → lactose + water
- α-glucose + fructose → sucrose +water
 |
| Disaccharides |
3. Properties:
- Sweet
- Soluble in water
- All disaccharides are non-reducing sugars except for lactose and maltose
- Hydrolysis of disaccharide forms hexoses
4. Functions of disaccharide:
- Carbohydrates in plants are mainly transported in the form of sucrose. This is because sucrose is soluble in water and is inert (inactive).
- Source of energy for organisms.
Chemical tests for sucrose
- Boil sucrose with solution of Fehling's solution. Result: negative.
- Hydrochloric acid is added to sucrose and boiled. Acid cause hydrolysis of sucrose into glucose and fructose. A small amount of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3 ) is added to neutralize the mixture. Fehling's is added to the mixture and then boiled. Result: Brick red precipitation is formed.
No comments:
Post a Comment