DNA - the hereditary material of life
Structure
- A DNA molecule consists of 2 polynucleotide chains coiled to form a double helix.
- The 2 chains are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. (T and A are complementary bases; while G and C are another complementary bases).
- Each complete turn of the double helix is 3.4nm long and contains 10 pairs of bases.
- The diameter of each helix is 1.0nm.
- The polynucleotide chains of DNA molecule are anti-parallel (the 5'end of one chain lies next to the 3' end of the other chain).
- the polynucleotide chain is made up of deoxyribonucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bonds.
Complementary base pairing
- Due to its structure, only purine bases can pair with pyrimidine bases.
- Adenine (A, a purine) pairs with thymine (T, a pyrimidine) with 2 hydrogen bonds.
- Guanine (G, a purine) pairs with cytosine (C, a pyrimidine) with 3 hydrogen bonds.
 |
| Complementary base pairing |
RNA
1. RNA is a polynucleotide. The monomer of RNA is ribonucleotide.
2. RNA molecule consists of one polynucleotide chain.
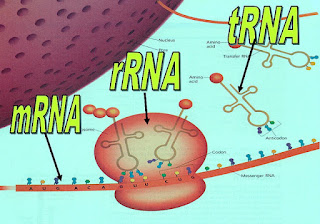
3. There are three types of RNA in cells:
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- messenger RNA (mRNA)
- transfer RNA (tRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
1. More than 80% of RNA in the cell is rRNA.
2. rRNA is found in ribosome. A ribosome is constructed from rRNA (50%) and protein (50%).
3. Functions of rRNA:
- Main component of ribosome.
- Bind mRNA molecule to ribosome during protein synthesis.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
1. The longest RNA molecules which contains 70 to 3,000 nucleotides.
2. mRNA molecules are long uncoiled molecules.
3. Function of mRNA:
- Carry genetic information from gene into the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
1. The shortest RNA molecules.
2. tRNA makes up about 10% to 15% of RNA in cells.
3. The polynucleotide chain is folded to form a 'clover-leaf'.
4. The anticodon of tRNA contains 3 bases which are complementary to the codon for the amino acid it carries.
5. Function of tRNA:
- Transfer a specific amino acid to ribosome for polypeptide synthesis.
 |
| rRNA, mRNA, tRNA |
Differences between RNA and DNA


No comments:
Post a Comment