Osmotic Pressure
- When a solution is separated from pure water by semi-permeable membrane, there will be net water moving across into the solution.
- The minimum pressure that has to be exerted by the solution to prevent water from moving in is called the osmotic pressure of the solution.
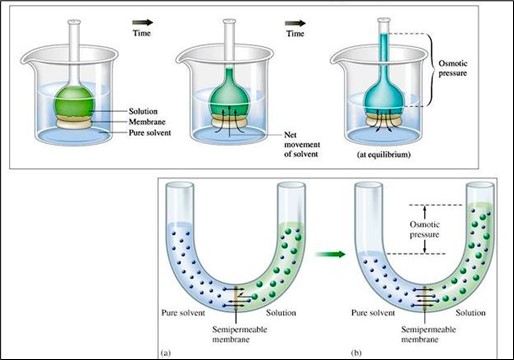 |
| Osmotic pressure examples |
Turgor Pressure
- Turgor pressure = the pressure of cytoplasm exerted against the walls of a turgid cell.
- This pressure is counteracted by the wall pressure.
Wall Pressure (Ψ p)
- Wall pressure = the pressure of the cell wall exerted against the cytoplasm of the plant cell.
- The wall pressure is also known as pressure potential (Ψ p) for plant cells.
- Pressure potential usually has a positive value.
 |
| The relationship between turgor pressure and wall pressure |
Water Potential (Ψ)
- Water potential = the potential of water to move out of a solution by osmosis.
- The water potential of a cell is the potential of water to move out of a cell through osmosis.
- Symbol = (Ψ) ; Unit = kPa (kiloPascal; 1kPa = 1000Pa) or MPa (MegaPascal), 1MPa = 100,000Pa)
- Pure water has the highest water potential. The water potential of pure water is 0 kPa at atmosphere pressure (101325 kPa).
- The water potential of a plant cell (Ψ) = solute potential (Ψ s) + pressure potential (Ψ p)
 |
| The water movement from a dilute to a concentrated solution |
Solute Potential (Ψ s)
- Solute potential = the potential of a solution to take in water by osmosis due to the presence of solute materials.
- Solute potential is also known as osmotic potential.
Water Potential for Solution (Ψ sol)
- (Ψ sol) = the potential of water to move out of a solution by osmosis.
- The water potential of a solution is negative in value.
- This is because water potential for pure water is 0 kPa and pure water has the highest water potential.
- Solution with larger negative water potential value have low water potential.
- For example, cell A with water potential of -0.5 kPa has higher water potential than cell B with water potential value of -0.9 kPa. Thus, water will flow from A to B.
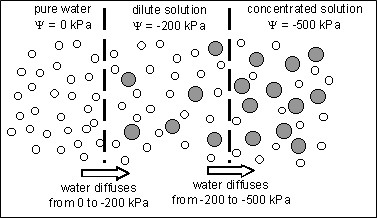 |
| The movement of water through different types of solution |
No comments:
Post a Comment