Organic compounds - chemical compounds that contain carbon (C) elements.
Monomers - building blocks for polymers
Polymers - materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules.
Organic Compounds in the Cell - Carbohydrates
 |
| Foods that contain carbohydrates |
- Made up of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen
- Ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in one molecule of carbohydrate is 2:1
- Importance: as storage and supply of energy
- 3 main types of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
 |
| 3 main types of carbohydrates |
Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)
- General formula: (CH2O)n , where n = 3 , 5 / 6 carbon atoms in the molecule
- Most common = 6-carbon sugar / hexoses (C6H12O6)
- Soluble in water, sweet, and form crystals
- Can combine with protein & lipids to form glycoproteins & glycolipids (part of plasma membrane)
- All monosaccharides are reducing sugar!!
- Examples:
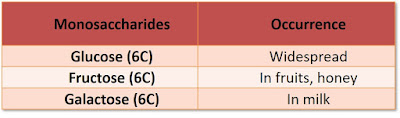 |
| Monosaccharides |
Disaccharides
- 2 monosaccharides form disaccharides, by removing a molecule of water (condensation)
- Formula: C12H22O11
- It can be broken down to monosaccharides by adding water (hydrolysis)
- Water soluble, sweet, form crystals
- Maltose and lactose are reducing sugar, sucrose is not !!
- Examples:
 |
| Disaccharides |
Polysaccharides
- Polymers that consisting of chains of monosaccharides
- General formula: (C6H10O5)n , where n varies from 40 to several thousands
- Can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides by heating with acid / enzymatic reactions
- Insoluble in water, ✗ sweet, cannot be crystallized
- Iodine solution is used to test for the presence of starch
- Examples:
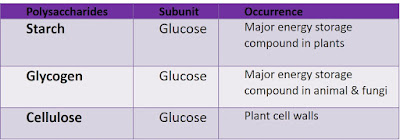 |
| Polysaccharides |
 |
| Condensation and hydrolysis |
★ Reducing Sugar ★ [Any carbohydrate whose structure contains an aldehyde, or a hemiacetal in equilibrium with an aldehyde]
Define: sugars that can act as reducing agents.
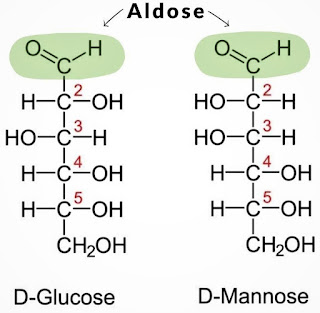 |
| Examples of reducing sugar's structure |
Test for a reducing sugar: Benedict’s solution
- When sugar solution is heated with Benedict’s solution, formation of a brick-red precipitate indicates a reducing sugar is present.
 |
| Benedict`s test |
No comments:
Post a Comment