1. The 2 nucleic acids in the cells are:
- DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- RNA (ribonucleic acid)
2. Nucleic acids are natural polymers. Nucleic acid monomers are nucleotides.
3. A nucleotide has 3 components:
- 5-carbon sugar (pentose)
- Organic base / nitrogenous base
- Phosphoric acid
 |
| Structure of nucleotide |
4. The pentose of nucleotides are ribose or deoxyribose.
5. Nucleotide containing ribose is called ribonucleotides (RNA monomers).
6. Nucleotide containing deoxyribose is called deoxyribonucleotide (DNA monomers).
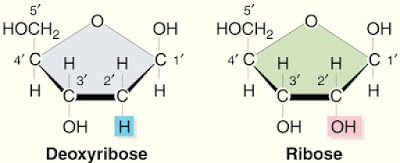 |
| Structure of ribose and deoxyribose |
7. Nucleotide has one of these five organic bases:
- adenine (A)
- guanine (G)
- thymine (T)
- cytosine (C)
- urasil (U)
8. These bases can be divided into 2 group:
- Purines (double-ringed molecule): Adenine, Guanine
- Pyrimidine (single-ringed molecule): Thymine, Cytosine, Uracil
 |
| 5 organic bases |
Formation of nucleotides and nucleic acid
- In formation of nucleotide, a nitrogenous base is first linked to pentose by condensation reaction to form nucleoside.
- Phosphate group is then added to the nucleoside to form a nucleotide.
- Nucleic acids are polynucleotides. Polynucleotides are formed by linking nucleotides together.
- Two nucleotides are linked together through condensation reaction to form dinucleotides.
- Further addition of nucleotides to dinucleotides will form polynucleotides.
- Nucleotides in polynucleotides are linked together in phosphodiester bonds.

Formation of phosphodiester bond - A nucleotide chain has 5' end and a 3' end. The 5' end of the polynucleotide chain is the end with the free phosphate group.
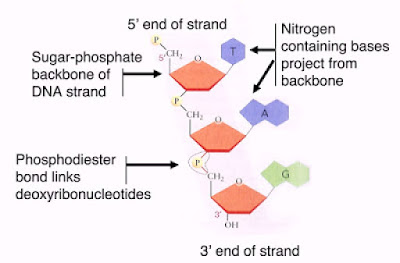 |
| 5' end and 3' end of nucleotide chain |
No comments:
Post a Comment