 |
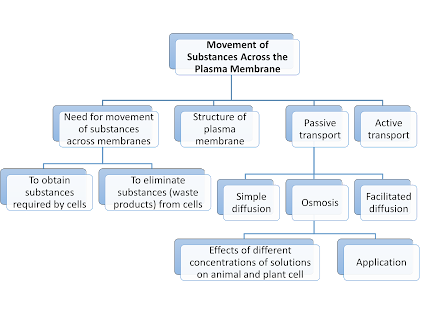
| SPM Biology 3 Movement of Substances Across the Plasma Membrane Mind Map |
- All the substances that are required by the cell (e.g. oxygen, water, mineral) have to be transported from the surroundings across the plasma membrane into the cell.
- All the waste products (e.g. carbon dioxide) have to pass through the plasma membrane to be excreted from the cell.
Structure of Plasma Membrane
Fluid Mosaic Model
A membrane is pictured as a mosaic because it has various protein molecules embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Since the membrane is fluid, most of the individual protein and phospholipid molecules can drift laterally (slow movement away from the normal or original position) in the membrane.
The structure of plasma membrane is comprised of:
- Phospholipid bilayer
- Various types of protein molecules
 |
| Fluid Mosaic Model |
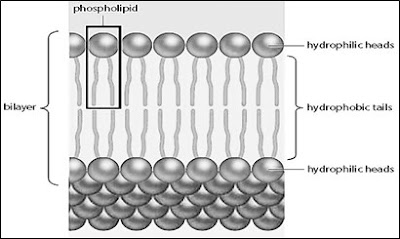
1. Phospholipid bilayer
- Is an amphipathic molecules (has both hydrophilic region and hydrophobic region).
- Polar head: hydrophilic (attracted to water).
- Non-polar tail: hydrophobic (repelled by water).
- Only allow some substances to cross the plasma membrane.
- Small molecules & neutral molecules (e.g. water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, lipid-soluble molecules) can cross the membrane easily.
Phospholipid bilayer
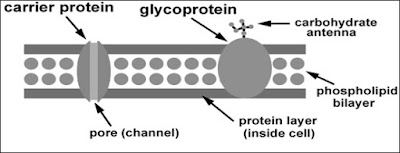
2. Protein molecules
- Slightly bigger polar molecules (e.g. glucose, amino acids, charged ion) can cross the plasma membrane with the help of protein molecules called transport protein.
- Transport proteins in the plasma membrane function as:-
- Carrier protein: a protein molecule that has a shape that fits the shape of a specific molecules so that it can only carry specific molecules across the membrane.
- Channel protein: a pore made of protein that provides a passage for a particular solute to pass through.
****Big molecules (e.g. sucrose, protein, starch) cannot move across the membrane****
No comments:
Post a Comment