1. Lipid is a compound that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But the ratio of hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms molecules is higher than 2:1.
2. All lipids are formed from fatty acids and glycerol.
3. Glycerol is a type of alcohol known as propane1,2,3-triol.
4. The structural formula for glycerol:
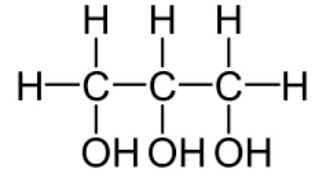 |
| Glycerol |
5. Fatty acid is carboxylic acid with long hydrocarbon chains. Fatty acid differs with the length of the hydrocarbon chain. It can be divided into 2 groups:
- Saturated fatty acids
- Unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated Fatty Acids
a. Saturated fatty acid does not have C=C bonds in their molecules.
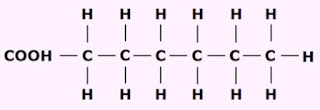 |
| Saturated fatty acid |
b. The common formula for this acid is RCOOH, where R= CnH2n+1 (R= CH3, C2H5...)
c. Examples of saturated fatty acids:
- Stearic acid
- Lauric acid
- Miristic acid
- Palmitic acid
- Aracidic acid
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
a. Unsaturated fatty acid has one or more double bonds C=C in the molecules.
 |
| Unsaturated fatty acid |
b. Example of unsaturated fatty acids:
- Oleic acid
- Linoleic acid
- Linolenic acid
- Arachidonic acid
- Palmitoleic acid
6. Non-essential fatty acids are fatty acids that can be synthesized by the body. For examples, oleic acid, stearic acid, cerotic acid and palmitic acid.
7. Essential fatty acids are fatty acids required by the body but are not synthesized by the body. For examples, linolenic acid, linoleic acid, and arachidonic acid.
8. Lipids are often referred to as alcohol ester because it is formed form acid and alcohol (glycerol).
 |
| Structure of alcohol ester |
9. Lipids can be classified into 3 major groups:
- Triglyceride
- Phospholipid
- Waxes
No comments:
Post a Comment