1. All fats and oils are triglycerides.
2. A triglyceride molecule is formed through condensation reaction between three fatty acids and one glycerol molecule.
3. Hydrolysis of a triglyceride molecule produces fatty acid molecules and glycerol molecule.
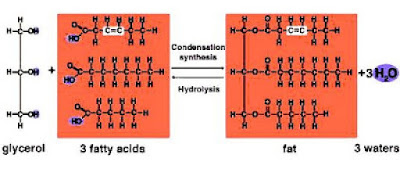 |
| Condensation and hydrolysis reactions of triglyceride |
4. Each fatty acid molecule is linked to glycerol by an ester bond, -COO.
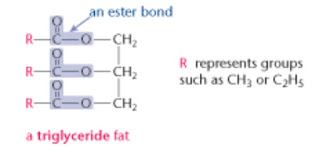 |
| Ester bond, -COO |
5. Saturated fat is a fat that does not contain any C=C bond in its molecule. Most of the saturated fat exists as solids in room temperature.
6. Unsaturated fat is a fat that has one or more C=C bonds in its molecule.
- Monounsaturated fat is fat with molecules that only has one double bond between its carbon atoms. For examples, sesame oil and groundnut oil.
- Polyunsaturated fat is fat with molecules that have two or more doubles C=C bonds in its molecules. For examples, maize oil, linseed oil and cottonseed oil.
- Polyunsaturated fat has a low boiling level, thus it exists as liquid in room temperature.
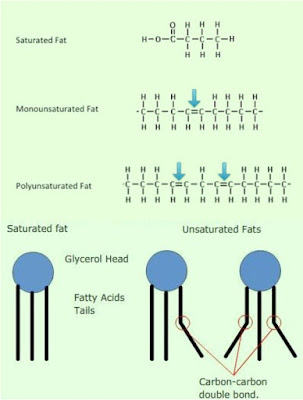 |
| Saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat molecules |
7. The consumption of food rich with saturated fat and cholesterol increases the risks of cardiovascular diseases. Saturated fat molecules and excess cholesterol deposit on the artery walls, thus narrowing it.
Physical properties of triglycerides
- Not soluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents.
- High relative molecular mass.
- High ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in molecule.
- Can be emulsified.
- Fat usually exists as a solid while oil exists as liquid at room temperature.
Chemical properties of triglycerides
- Triglycerides undergo hydrolysis to form fatty acids and glycerol.
Distribution of triglycerides in organisms
- In adipose tissues underneath the skin.
- Attached to the surface of visceral organs such as the heart, liver and digestive tracts.
- In eggs.
- In seeds (maize, peanuts and etc.).
Functions of triglycerides
- Source of energy of organisms.
- As food and energy stores for animals.
- Major components of plasma membrane.
- Heat insulation. Fat underneath the skin is a heat insulator for animals in cold region.
- Water proofing. Oils and waxes on the outer surface of organisms waterproof the body.
- Protection. Fats packed around visceral organs protect these organs.
- Fat is a source of metabolic water for animals.
- Fat is an important solvent for vitamins A,D,E,K and hormones in the body.
- Saturated fat is the raw material for synthesizing cholesterol.
- Buoyancy. Stored fats also aid buoyancy.
No comments:
Post a Comment