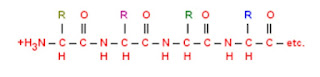
1. Two amino acids can linked together to form a dipeptide by a condensation reaction. In the dipeptide, the two amino acids are linked by a peptide bond.
2. Peptide bond can only be formed by condensation reaction between the carboxyl group of one and the amino group of another amino acid.
3. Further amino acids can be added on either end of the dipeptide to form a polypeptide. Proteins consists of one or more polypeptides.
 |
| Polypeptide chain |
Structure of protein
- A protein may contain up to 20 types of amino acids.
- Amino acids in proteins are linked together by peptide bond.
- Proteins are polymers with a large relative molecular mass.
- Protein molecules may contain one or more polypeptide chains.
- A polypeptide chain has a carboxyl group, COOH at one end and an amino group, NH2 at the other end (refer to the diagram above).
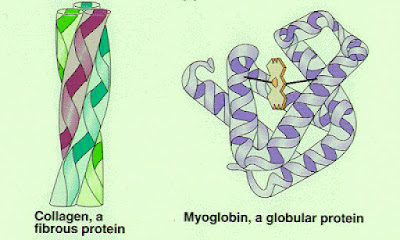
Fibrous proteins
(a) In fibrous proteins, the polypeptide chains exist as long parallel helixes. Helixes are cross-linked by:
- hydrogen bonds,
- disulphide bonds, or
- electrovalent bonds
(b) Examples of fibrous proteins are collagen, keratin and fibrin.
Globular proteins
(a) In globular protein, the polypeptide chains (helix) are tightly folded to form a globular molecules.
(b) The globular structure is stabilized by cross links, such as disulphide bonds.
(c) Examples of globular proteins include enzymes, myoglobin, insulin and hemoglobin.
fibrous protein globular protein
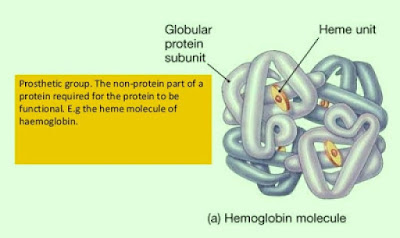
Conjugated proteins
(a) A protein may conjugate with prosthetic groups such as lipid, polysaccharides, nucleic acid, metals and ions.
(b) Examples of conjugated proteins are lipoprotein, nucleoprotein, glycoprotein and hemoglobin.
Functions of protein
- Protein is an important structural construction material.
- Protein can also function as catalyst. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
- Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Transport proteins include hemoglobin, the carrier of oxygen in blood.
- Maintain pH of cytoplasm and blood.
- Proteins are stored in organisms for food and energy.
- Protein is also involved in the defense and protection of body against pathogens. Antibodies are proteins in the blood that destroys pathogens. Fibrinogen and prothrombin are involved in blood clotting. Mucus protects the epithelial layer of digestive organs.
- Functions as hormones. Insulin, prolactin, and thyroxin are all proteins.
- Protein is also involved in food digestion. Digestive enzymes are proteins.
- Proteins play an important role in movements and mobility. Actin and myosin are involved in muscle contraction and movements of an amoeba.
- Protein such as thyroxine is important for growth.

Great job for publishing such a beneficial web site. Your web log isn’t only useful but it is additionally really creative too. There tend to be not many people who can certainly write not so simple posts that artistically. Continue the nice writing adsorbent manufacturers
ReplyDelete