1. Molecular formula: (C6H10O5)n
2. Plant stores starch and animals stores glycogen. Glycogen is referred to as "animal starch".
3. Physical properties:
- not soluble in water.
- not sweet.
- cannot crystallize.
- high molecular mass.
4. Chemical properties:
- undergoes hydrolysis to become glucose.
- reacts with iodine solution to form a purplish red color.
5. Distribution of glycogen (mainly):
- liver
- muscles
- brain
6. Structure of glycogen:
- Glycogen has branched-chain molecules. The structure of glycogen molecule is similar with amylopectin, but glycogen molecule has more branches.
- Glycogen molecules are built from α-glucose molecules that are linked together by 1,4-glycosidic bond. Branches are linked by 1,6-glycosidic bonds.
- The chain are coiled into helix.
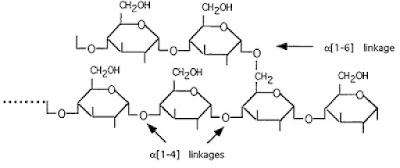 |
| Glycogen structure |
7. Functions:
- Glycogen is storage carbohydrate in animals.
- Source of energy for animals.
Properties and structure of glycogen related to its function
1. Glycogen is a storage compound. It is due to:
- It is not soluble in water. Thus, stored glycogen does not change the osmotic pressure of the organ.
- Glycogen molecules are compact. A large mass can be stored in a small space.
2. Glycogen is a source of energy for animals. Glycogen can carry out this function because it can undergo hydrolysis to form glucose. Glucose is the substrate for respiration.
No comments:
Post a Comment