Unicellular Organisms
Made up of only one cell.
Is a complete unit of life that can carry out all life processes.
Simplest form = Protozoans
Examples: Ameoba sp., Paramecium sp.
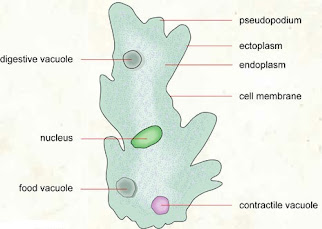 | ||
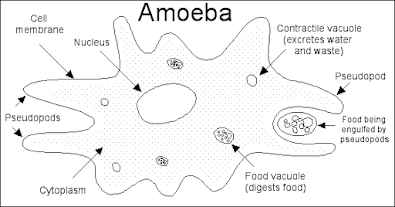
Structure of Ameoba sp.
|
Life processes carried out by unicellular organisms
1. Respiration- Exchange of gases (oxygen & carbon dioxide) occur through plasma membrane by simple diffusion (the transport of molecules across the plasma membrane down the concentration gradient through the phospholipid bilayer until equilibrium is reached) on the surface of cell.
- Amoeba sp, moves using pseudopodium (false feet).
- Paramecium sp. moves using rhythmic cilia beats.
3. Nutrition
- Amoeba sp. moves towards food by extending its pseudopodium to trap food particles by phagocytosis.
- Food vacuole combines with lysosome, food particles are hydrolyzed by the enzyme lysozyme in lysosomes.
- Nutrient are absorbed into cytoplasm.
- Undigested food is discharged when Amoeba sp, moves
- For Paramecium sp., cilium beat helps to transfer food particles into oral groove. Undigested food is discharged through anus.
- Respond to chemicals, touch or bright light by moving away from the stimuli.
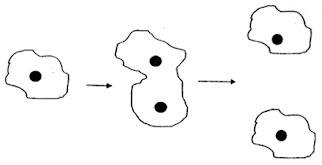
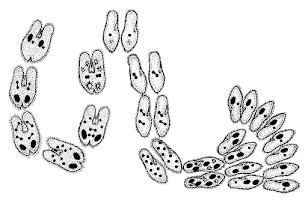
5. Reproduction
- Reproduce via binary fission (asexual reproduction) through mitosis when the conditions are suitable and have plenty of food.
- Amoeba sp. forms spores when conditions are bad (dry, low temperature, food shortage)
- For Paramecium sp., conjugation (sexual reproduction) occurs when conditions are bad
6. Growth
- Synthesize new cytoplasm.
7. Excretion
- Waste (carbon dioxide, ammonia etc.) are removed by diffusion/
- Water diffuse via osmosis.
- Undergo osmoregulation = the process of maintenance of salt and water balance ( osmotic balance) across membranes within the body`s fluids


No comments:
Post a Comment