SPM Biology 2 Cell Biology & Organization Part 2 Cell Structure & Functions
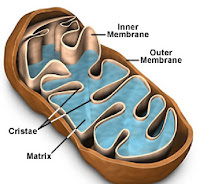 |
| Mitochondrion |
Mitochondrion (Plural: Mitochondria)- Rod-shape / spherical
- 2 layers of membranes
- Functions:
- A site that generates energy
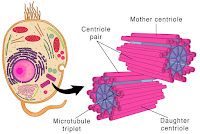 |
| Centriole |
Centriole- Small cylindrical components that exist in pairs in animal cells, X in plant cells
- Made up of microtubules
- Functions:
- Forms spindle fiber during cell division
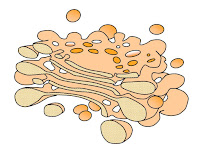 |
| Golgi Apparatus |
Golgi Apparatus
- Stack of parallel flattened sacs, single cell membrane
- Functions:
- Processes, modifies, packs and transports chemicals (protein, carbohydrate etc.)
Plasma Membrane
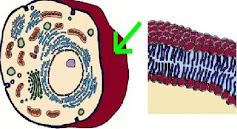 |
| Plasma Membrane |
Outer membrane that surrounds the cell- Made of proteins & phospholipids
- Thin, elastic
- Functions:
- Controls movement of substances into & out of the cell
- Separates content of cell from external environment
- Allows exchange of nutrients, gases and waste materials between cells & their surroundings
 |
| Lysosome |
Lysosome- Small spherical sac, single membrane
- Contains hydrolytic enzymes
- Functions:
- Hydrolyses complex organic molecules (protein, nucleic acid & lipid)
- Breaks down bacteria, damaged cells
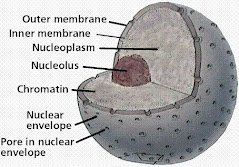 |
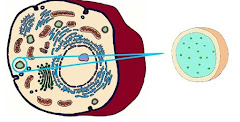
| Nucleus |
Nucleus (Plural: Nuclei)- Largest component in the cell
- Spherical, enclosed in nuclear membrane with many pores
- Double membrane
- Contains chromosomes, nucleolus and nucleoplasm
- Functions:
- Controls all cell activities
- Chromosomes contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
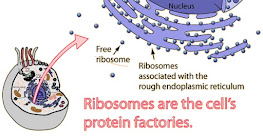 |
| Ribosome |
Ribosome- Small, compact, spherical granules
- Consists protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Present on the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum / freely exist in cytoplasm
- Function:
- Site for protein synthesis
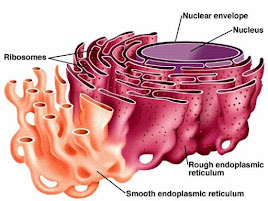 |
| RER & SER |
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)- Folded flattened sacs
- Two types of ER
- Rough ER: has ribosomes attached on the surface
- Smooth ER: X ribosomes
- Functions:
- Act as transport system within the cell
- RER transports proteins synthesized by ribosomes
- SER synthesizes & transports glycerol and lipids, detoxify drugs and metabolic by-products
 |
Cytoplasm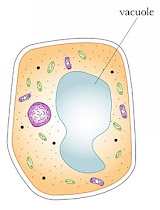 | | Vacuole |
|
Cytoplasm
- Jelly-like medium that contains the components of cells
- Contain organic (protein, carbohydrate etc.) & inorganic (potassium ions) compounds
- Functions:
- Medium for biochemical reactions in cells
Vacuole
- Liquid-filled sac, the liquid called cell sap
- Surrounded by tonoplast
- Exist in plant cells
- Small size in unicellular animals
- Functions:
- Water is absorbed into the vacuole and the plant cell becomes turgid
- In unicellular animals, vacuole contracts during osmoregulation, osmosis and excretion
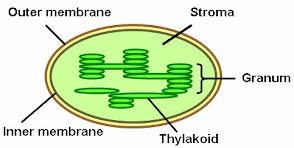 |
| Chloroplast |
Chloroplast- Oval shaped
- 2 layers of membrane
- Contains chlorophyll
- Functions:
- Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight during photosynthesis
Cell Wall
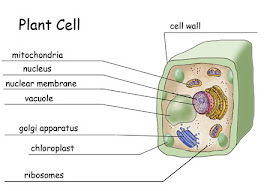 |
| Cell Wall |
- Strong and rigid outer layer of plant cells
- Made from cellulose fiber
- Fully permeable
- Functions:
- Maintains the shape of plant cells
- Provides mechanical support to plant cells












No comments:
Post a Comment